Introduction
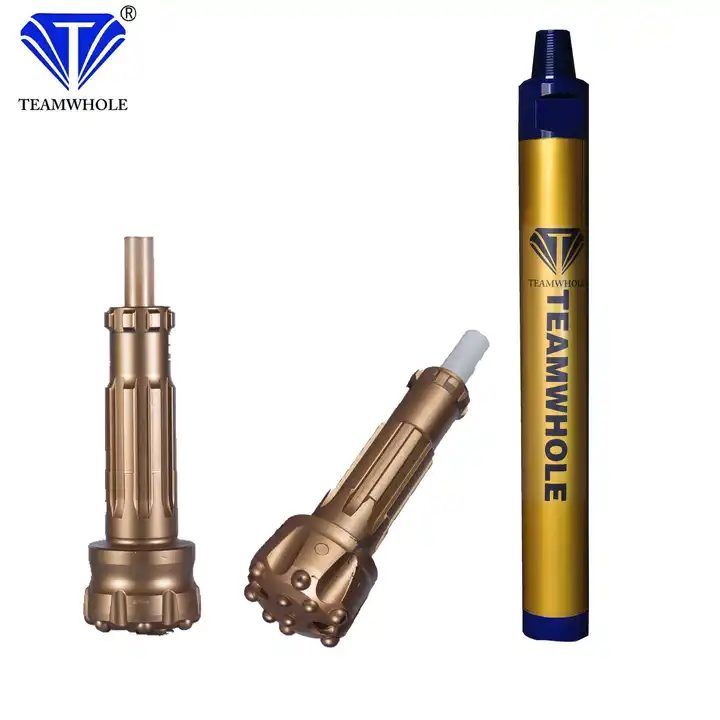

In the mining world, the longevity of drill bits is crucial for efficient and cost-effective operations. Tianhe, a leading geotechnical drilling manufacturer, understands the importance of maximizing the lifespan of mining drill bits. With their research, design, and production expertise, Tianhe offers valuable tips and strategies for ensuring long-lasting drill bits. However, before diving into these expert tips, it's essential to understand the common causes of drill bit wear.
Importance of Extending Lifespan of Mining Drill Bits
Extending the lifespan of mining drill bits is essential for several reasons, primarily related to improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring the safety and productivity of mining operations. Here's why it's important to focus on extending the lifespan of mining drill bits:
- Cost Savings: Mining drill bits represent a significant investment for mining companies. Extending their lifespan directly translates into cost savings by reducing the frequency of bit replacements and the associated expenses, including purchasing new bits, downtime for replacement, and labor costs.
- Increased Productivity: Longer-lasting drill bits mean less downtime for changing worn-out bits and more time spent on actual drilling operations. This increased uptime leads to higher productivity levels, allowing mining operations to extract more ore or material within a given timeframe, ultimately improving profitability.
- Improved Efficiency: Worn or dull drill bits are less efficient at cutting through rock and ore formations, leading to slower drilling speeds and reduced overall efficiency. Extending the lifespan of drill bits ensures that they maintain their sharpness and cutting effectiveness for longer periods, maximizing drilling efficiency and performance.
- Optimized Equipment Utilization: By prolonging the lifespan of drill bits, mining companies can optimize the utilization of drilling equipment, such as drills and rigs. Reduced downtime for bit changes means that equipment can operate longer, leading to better asset utilization and improved return on investment (ROI) for mining equipment.
- Enhanced Safety: Worn or damaged drill bits can compromise the safety of mining operations by increasing the risk of equipment failure, unplanned downtime, and accidents. Extending the lifespan of drill bits helps maintain equipment integrity and reliability, reducing the likelihood of failures or incidents that could endanger workers' safety.
- Minimized Environmental Impact: Mining operations can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat disruption, soil erosion, and pollution. Extending the lifespan of drill bits reduces the need for manufacturing new bits, resulting in lower resource consumption, energy usage, and waste generation, ultimately minimizing the environmental footprint of mining activities.
- Improved Operator Satisfaction: Mining drill operators often work in challenging and demanding conditions. Providing them with longer-lasting drill bits reduces the frequency of bit changes and associated maintenance tasks, improving overall job satisfaction and morale among operators.
- Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility: Extending the lifespan of mining drill bits aligns with sustainability and corporate responsibility principles by promoting resource conservation, waste reduction, and efficient resource utilization. It demonstrates a commitment to responsible mining practices and environmental stewardship.
Extending the lifespan of mining drill bits is essential for cost savings, increased productivity, improved efficiency, optimized equipment utilization, enhanced safety, minimized environmental impact, operator satisfaction, and sustainability. By implementing strategies to prolong the lifespan of drill bits, mining companies can achieve better operational outcomes and contribute to long-term success in the mining industry.
Tianhe's Expert Tips for Long-Lasting Drill Bits
Tianhe's expertise in geotechnical drilling equips them with valuable insights into maintaining the longevity of drill bits. From choosing the right type of bit to implementing proper maintenance techniques, Tianhe offers comprehensive guidance on extending the lifespan of various types of drill bits, such as rock drill bits, rotary drilling bits, water well drill bits, and more.
Common Causes of Drill Bit Wear
Drill bit wear is a natural phenomenon that occurs during drilling operations due to various factors. Understanding the common causes of drill bit wear is crucial for implementing preventive measures and optimizing drilling performance. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Abrasion: Abrasion occurs when the drill bit comes into contact with the rock or ore formation being drilled. The abrasive properties of the material being drilled can gradually wear down the cutting edges and surfaces of the bit, leading to diminished cutting effectiveness and increased wear over time.
- Impact Load: Impact load refers to the force exerted on the drill bit as it penetrates the rock or ore formation. High-impact loads, such as those encountered in hard or dense formations, can cause stress and deformation of the bit's cutting edges and surfaces, leading to accelerated wear and potential damage.
- Heat Generation: Heat generation during drilling operations can accelerate wear on drill bits, particularly in high-speed or continuous drilling applications. Friction between the bit and the rock generates heat, softening the bit material and reducing its hardness, leading to increased wear and diminished cutting performance.
- Erosion: Erosion occurs when abrasive particles in the drilling fluid or formation wear away the surfaces of the drill bit. This is particularly common in formations with high levels of sand, gravel, or other abrasive materials and in drilling operations using high-pressure fluid systems.
- Chemical Reaction: Some rock formations may contain minerals or chemicals that react with the materials used in drill bit construction, leading to chemical wear. This can result in corrosion or degradation of the bit's cutting surfaces and materials, reducing their durability and lifespan.
By addressing these common causes of drill bit wear through proper equipment selection, maintenance, and operational practices, mining and drilling companies can minimize wear-related issues, optimize drilling performance, and extend the lifespan of their drill bits. Regular inspection, maintenance, and replacement of worn or damaged bits are also essential for ensuring safe and efficient drilling operations.
Choosing the Right Drill Bits
When selecting the right mining drill bits, it's crucial to understand the different types available. Tianhe offers many options, including diamond core bits, PDC bits, and tricone bits, each designed for specific drilling conditions and rock formations. Choosing the appropriate type for your project ensures optimal performance and longevity for your mining drill bits.
Factors to consider when selecting rock drill bits include the hardness of the rock formations you'll be drilling into and the type of drilling technique you'll be using. Tianhe's expert team can provide valuable insights into which rock drill bits are best suited for different geological conditions, helping you make informed decisions that will extend the lifespan of your equipment.
The quality of materials used in rotary drilling bits is paramount to their performance and durability. Tianhe takes pride in utilizing high-grade carbide and steel materials in its manufacturing process, ensuring that its rotary drilling bits can withstand tough drilling environments while maintaining exceptional performance.
By understanding the various types of mining drill bits available and considering factors such as rock formation hardness and drilling techniques when selecting rock drill bits, as well as prioritizing quality materials in rotary drilling bits, you can make informed choices that will maximize the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. With Tianhe's expertise and high-quality products, you can easily tackle any drilling project.
Proper Maintenance and Cleaning

Proper maintenance and cleaning are essential for extending the lifespan of mining drill bits. Tianhe, a leading geotechnical drilling manufacturer, emphasizes the importance of regular inspection, effective cleaning techniques, and proper storage to ensure optimal performance.
Regular Inspection of Mining Drill Bits
Regular inspection of mining drill bits is crucial in identifying any signs of wear and tear. Tianhe recommends conducting thorough visual inspections after each use to check for any damage or dullness in the cutting structure. Additionally, periodic wear profile measurements can help determine when it's time for replacements or repairs.
Effective Cleaning Techniques for Water Well Drill Bits
Proper cleaning is key to maintaining their efficiency when it comes to water well drill bits. Tianhe advises using high-pressure air or water to remove any debris or rock particles that may have accumulated during drilling operations. This helps prevent corrosion and ensures the bits remain sharp and ready for use.
After using high-pressure air or water to remove debris and rock particles from water well drill bits, it is important to thoroughly dry the bits before storing them. Moisture left on the bits can lead to rust and corrosion, reducing lifespan and effectiveness. Proper storage in a clean, dry environment is essential for maintaining the quality of the drill bits. This will help ensure that they are ready for use whenever needed, without extensive cleaning or maintenance.
Importance of Proper Storage for Mining Drill Bits
Proper storage is often overlooked but plays a significant role in preserving the quality of mining drill bits. Tianhe recommends storing the drill bits in a clean, dry environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This helps prevent rusting and deterioration, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the bits.
By following these maintenance and cleaning tips from Tianhe, you can ensure that your mining drill bits remain in top condition for longer, ultimately maximizing their performance and longevity.
Correct Operation Techniques

When maximizing the lifespan of your water well drilling bits, the impact of the drilling technique cannot be overstated. You can significantly reduce wear and tear on your mining drill bits by employing proper drilling techniques, such as using the appropriate speed and pressure. Tianhe's experts emphasize the importance of training operators on the correct operation techniques to ensure the longevity of water drill bits.
Impact of Drilling Technique on Lifespan of Water Well Drilling Bits
How drilling is carried out directly impacts the lifespan of water well drilling bits. Utilizing excessive force or speed can lead to premature wear and damage to the mining bits, ultimately reducing longevity. Tianhe recommends implementing controlled and precise drilling techniques to minimize stress on the drill bits and extend their lifespan.
Ensuring Proper Lubrication for Water Drill Bits
Proper lubrication is essential for maintaining the performance and durability of water drill bits. Inadequate lubrication can increase friction and heat, accelerating wear on mining drill bits. Tianhe's high-quality lubricants are designed to reduce friction and heat generation, ensuring optimal performance and prolonged lifespan for water well drilling bits.
Avoiding Overheating and Overexertion of Mining Bits
Overheating and overexertion are common issues that can significantly diminish the lifespan of mining drill bits. To prevent overheating, monitoring temperature levels during operation and taking necessary breaks to allow the drill bits to cool down is crucial. Additionally, avoiding overexertion by using appropriate pressure levels during drilling helps prevent premature wear on water well drilling bits.
To further prevent overheating and overexertion of mining drill bits, it is important to use the correct type of lubricant during operation. Using a high-quality lubricant can help reduce friction and heat buildup, thus extending the lifespan of the drill bits. Additionally, regularly inspecting and maintaining the drilling equipment can help identify any issues that may lead to overheating or overexertion, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
Monitoring Wear and Tear

Signs of Wear and Tear in Mining Drill Bits
Mining drill bits are subjected to intense wear and tear during operation, which can compromise their effectiveness. Signs of wear include dull or chipped cutting edges, decreased drilling speed, and increased vibration during operation. Monitoring these signs closely is crucial to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Importance of Timely Replacements for Water Drill Bits
For water well drilling bits, timely replacements are essential to maintain efficiency and prevent costly downtime. As the bits wear down, they become less effective at penetrating rock formations, leading to longer drilling times and increased energy consumption. Replacing worn bits promptly can minimize operational disruptions and maximize productivity.
Utilizing Tianhe's Wear Indicators for Mining Bits
Tianhe offers advanced wear indicators that provide real-time feedback on the condition of mining drill bits. These indicators use cutting-edge technology to measure the extent of wear on the bit's surface, allowing for proactive maintenance and timely replacements. By leveraging Tianhe's innovative wear indicators, operators can optimize their drilling processes and extend the lifespan of their mining bits.
By utilizing Tianhe's wear indicators for mining bits, operators can proactively identify potential issues before they escalate, saving time and money in the long run. The real-time feedback these advanced indicators provide allows for quick decision-making and efficient maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. This proactive approach to bit maintenance also helps to ensure the safety of the drilling operation and reduces the risk of unexpected failures.
Implementing Preventive Measures

Utilizing Tianhe's Advanced Coating Technologies for Mining Drill Bits
When it comes to extending the lifespan of your mining drill bits, Tianhe's advanced coating technologies are a game-changer. These innovative coatings provide an extra layer of protection, reducing friction and wear during drilling operations. Utilizing these cutting-edge coatings can significantly enhance the durability and performance of your rock drill bits, rotary drilling bits, and water well drill bits.
Importance of Regular Bit Sharpening for Extended Lifespan
Regular bit sharpening is crucial for maintaining the longevity of your mining drill bits. Tianhe recommends a routine sharpening schedule to ensure your drill bits remain in top condition. By keeping your water well drilling bits and mining bits sharp, you can minimize wear and tear while maximizing drilling efficiency, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of your equipment.
How Tianhe's Innovative Designs Improve the Longevity of Mining Bits
Tianhe's commitment to innovation is evident in its designs, engineered to enhance mining drill bits' longevity. With features such as optimized flute geometry and advanced cutting structures, Tianhe's designs minimize stress on the tool while maximizing drilling performance. Investing in these innovative designs for your water drill bits and mining bits can achieve superior durability and extended lifespan.
Tianhe's Proven Strategies for Prolonging Drill Bit Lifespan

In conclusion, maximizing the performance of your mining drill bits is crucial for the success of any drilling operation. By implementing Tianhe's proven strategies for prolonging drill bit lifespan, you can ensure that your equipment remains in top condition for longer. Taking the next step in extending the longevity of your mining bits involves regular maintenance, proper operation techniques, and utilizing advanced coating technologies to enhance durability.
Maximizing the Performance of Your Mining Drill Bits
To maximize the performance of your mining drill bits, it's essential to choose the right type for your specific drilling needs and ensure they are made from high-quality materials. Proper maintenance and cleaning, as well as correct operation techniques, can also significantly extend their lifespan. By implementing these strategies, you can optimize the performance of your mining drill bits and achieve more efficient and productive drilling operations.
Tianhe's expertise in geotechnical drilling has led to the development of advanced coating technologies that enhance the durability and longevity of mining drill bits. Their innovative designs and high-quality materials ensure that their products are built to withstand harsh drilling conditions, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of these essential tools.
Taking the Next Step in Extending the Longevity of Your Mining Bits
The next step in extending the longevity of your mining bits involves implementing preventive measures such as regular bit sharpening and utilizing Tianhe's wear indicators to monitor wear and tear. By staying proactive in maintaining and caring for your mining drill bits, you can extend their lifespan and maximize their performance throughout various drilling operations.
The next step in extending the longevity of your mining bits involves implementing preventive measures such as regular bit sharpening and utilizing Tianhe's wear indicators to monitor wear and tear. By staying proactive in maintaining and caring for your mining drill bits, you can extend their lifespan and maximize their performance throughout various drilling operations.
Additionally, investing in high-quality bits made from durable materials can significantly contribute to their longevity, reducing the frequency of replacements and downtime. Furthermore, conducting regular inspections and maintenance checks on your drilling equipment can help identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and adjustments to prevent further damage.

